Developer Instructions
Installing specific hardware support
Generic instructions for raspbian 2018-06-27 or later
Download the pre-build Raspbian (both lite and pixel available) for the balenaFin at this link
Flash (we suggest using balenaEtcher) and boot your device.
balenaOS/balenaCloud instructions
- Download the balenaFin (CM3) device type image (on balenaCloud, create a balenaFin (CM3) fleet first):
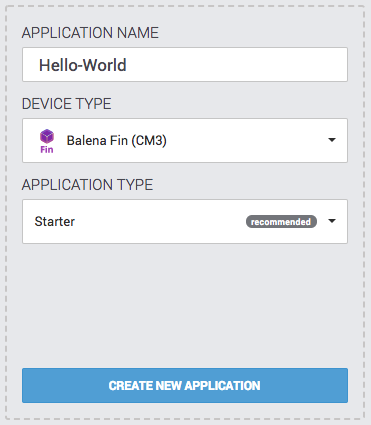
- Flash (we suggest using balenaEtcher and boot your device.
Controlling Bluetooth and WiFi
From within balenaOS (HostOS), the rfkill command can be used to:
- List all wireless controllers
rfkill list
- Soft disable the Wireless LAN (WiFi)
rfkill block wifi
- Soft disable the Bluetooth
rfkill block bluetooth
Note, these commands DO NOT disable the physical hardware. It is only possible to disable the radio interfaces with software.
Programming the co-processor on balenaFin
The co-processor's SWDIO interface is exposed to the compute module via an FTDI FT2232H-56Q JTAG-USB controller.
The co-processor can be flashed from the compute module.
We provide a balenaBlock for flashing the co-processor, the fin-block. The functionality for flashing the co-processor will be broken out into a standalone NodeJS package (in development).
Using the RTC from CM3L/CM3+L
The balenaFin sports a very common I2C RTC module that is well known, supported, and documented within the Raspberry Pi ecosystem: the DS1307.
There are plenty of guides on how to interact with the chip, including the following:
- https://learn.adafruit.com/adding-a-real-time-clock-to-raspberry-pi/set-rtc-time
- https://thepihut.com/blogs/raspberry-pi-tutorials/17209332-adding-a-real-time-clock-to-your-raspberry-pi
Controlling the RGB LED
echo 504 > /sys/class/gpio/export # (Red)
echo 505 > /sys/class/gpio/export # (Green)
echo 506 > /sys/class/gpio/export # (Blue)
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio504/direction
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio505/direction
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio506/direction
Now that you have the 3 GPIO LED pins ready, you can define your target color by setting each LED to high or low. For example, to turn the RGB off:
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio504/value
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio505/value
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio506/value
Toggling the Status LED bank
This device sports 9 status LEDs varying from power, eMMC, ethernet, WiFi, WAN, etc. There is a switch which allows users to toggle them all on and off via software.
exp_base=$(cat /sys/devices/platform/i2c*/i2c-*/*-0020/gpio/*/base)
led_gpio=$(expr $exp_base + 7)
echo ${led_gpio} > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${led_gpio}/direction
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${led_gpio}/value # turn off
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${led_gpio}/value # turn on
Cellular via mPCIe card
We are working on identifying and documenting cards known to work out of the box on the board. If you plan on adding LTE capability to the device, we suggest the Quectel EC21-XX Mini PCIe: the card is known to work out of the box, hence only APN configuration is required. On balenaOS (2.0.0+) you do so by adding a NetworkManager profile in the boot partition under the "system-connections" folder. You can find more info about this on our docs at: https://balena.io/docs/deployment/network/2.0.0/#cellular-modem-setup.
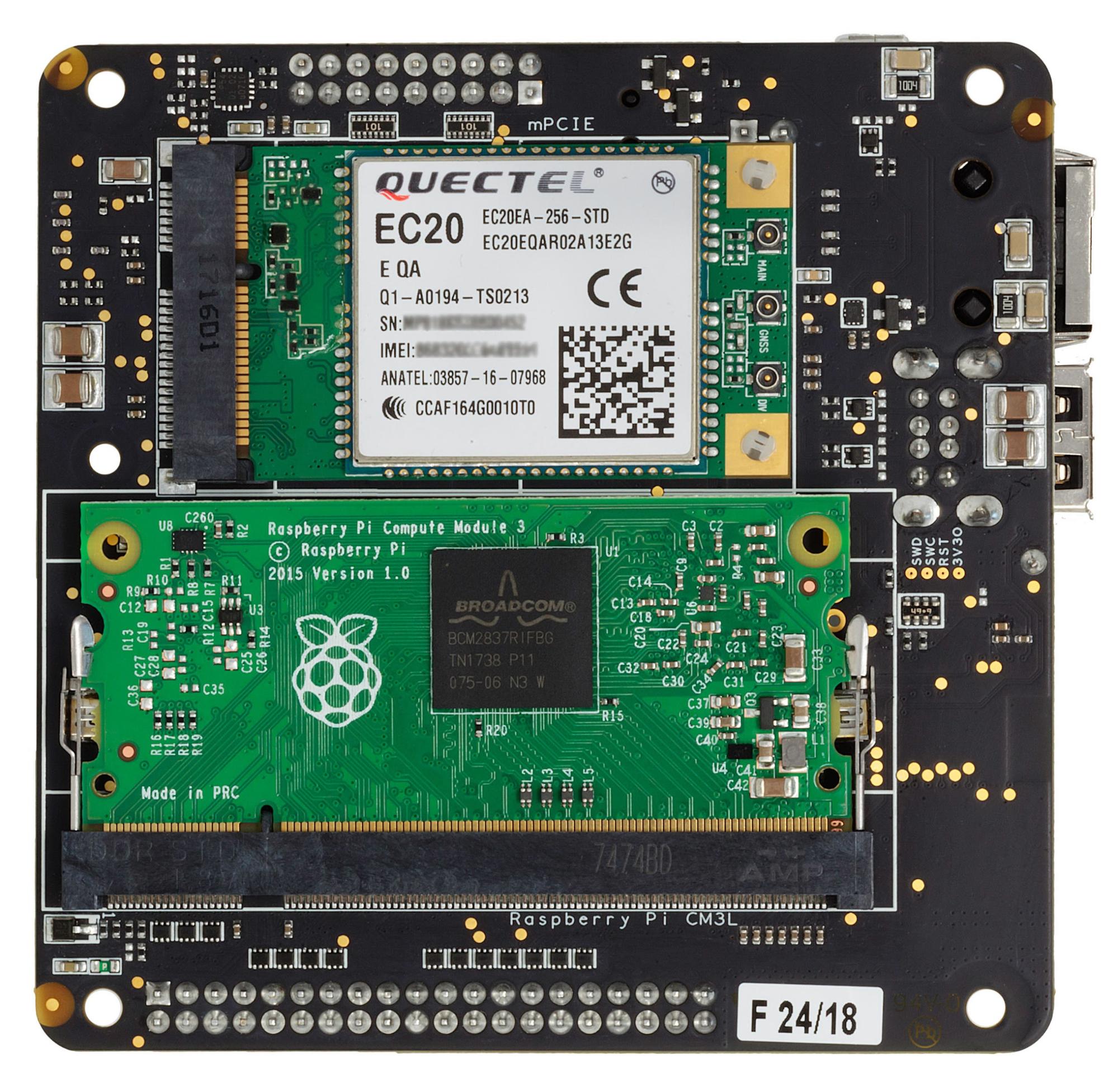
Reset mPCIe radio cards
exp_base=$(cat /sys/devices/platform/i2c*/i2c-*/*-0020/gpio/*/base)
mpcie_perst_gpio=$(expr $exp_base + 5)
echo ${mpcie_perst_gpio} > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${mpcie_perst_gpio}/direction
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${mpcie_perst_gpio}/value # mPCIe PERST on
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${mpcie_perst_gpio}/value # mPCIe PERST off
Disabling RF activity on mPCIe radio cards
exp_base=$(cat /sys/devices/platform/i2c*/i2c-*/*-0020/gpio/*/base)
radio_gpio=$(expr $exp_base + 4)
echo ${radio_gpio} > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${radio_gpio}/direction
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${radio_gpio}/value # mPCIe W-DISABLE on
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${radio_gpio}/value # mPCIe W-DISABLE off
Disabling HDMI
exp_base=$(cat /sys/devices/platform/i2c*/i2c-*/*-0020/gpio/*/base)
hdmi_gpio=$(expr $exp_base + 3)
echo ${hdmi_gpio} > /sys/class/gpio/export
echo "out" > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${hdmi_gpio}/direction
echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${hdmi_gpio}/value # HDMI off
echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio${hdmi_gpio}/value # HDMI on
Power saving
- Turn off HDMI when not required
- Turn off the STATUS LEDs bank
- Programmatically disable RF activity on mPCIe when not required (assumes a cellular modem is being used)
- Programmatically power on and off the CM3L/CM3+L when not required via the co-processor PIN PC9 (5V interface) and PIN PF5 (3.3V interface). This is the equivalent of unplugging power from the Raspberry Pi
NOTE: A firmata-based firmware and client library is under development. This will allow users to easily interact with the co-processor from the CM3L/CM3+L without needing to write their own firmware.